Surface mesh point queries: C API¶
Quest provides the in/out and distance field queries to test a point against a surface mesh. These queries take a mesh composed of triangles in 3D and a query point. The in/out query tests whether the point is contained within the surface mesh. The distance query calculates the signed distance from the query point to the mesh.
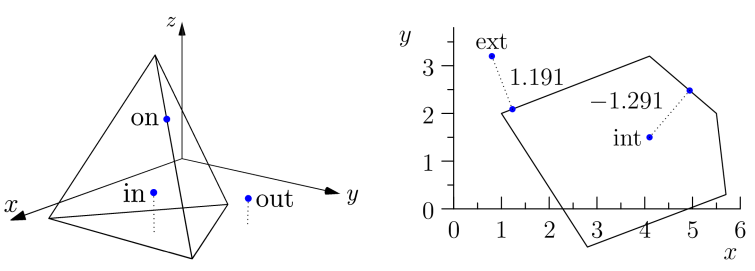
Fig. 27 Types of point-vs-surface-mesh queries provided by Quest. Left: In/out query, characterizing points as inside or outside the mesh. Points that lie on the boundary might or might not be categorized as inside the mesh. Right: Distance query, calculating the signed distance from each query point to its closest point on the mesh. A negative result indicates an interior query point.
The following examples show Quest’s C interface to these queries. The general
pattern is to set some query parameters, then pass a mint::Mesh * or file
name string to an initialization function, call an evaluate function
for each query point, then clean up with a finalize function.
In/out C API¶
The in/out query operates on a 3D surface mesh, that is, triangles forming a
watertight surface enclosing a 3D volume. The in/out API utilizes integer-valued
return codes with values quest::QUEST_INOUT_SUCCESS and
quest::QUEST_INOUT_FAILED to indicate the success of each operation.
These examples are excerpted from <axom>/src/axom/quest/examples/quest_inout_interface.cpp.
To get started, we first include some header files.
#include "axom/quest/interface/inout.hpp"
#ifdef AXOM_USE_MPI
#include <mpi.h>
#endif
Before initializing the query, we can set some parameters, for example, to control the logging verbosity and to set a threshold for welding vertices of the triangle mesh while generating the spatial index.
// -- Set quest_inout parameters
rc = quest::inout_set_verbose(isVerbose);
if(rc != quest::QUEST_INOUT_SUCCESS)
{
cleanAbort();
}
rc = quest::inout_set_vertex_weld_threshold(weldThresh);
if(rc != quest::QUEST_INOUT_SUCCESS)
{
cleanAbort();
}
By default, the verbosity is set to false and the welding threshold is
set to 1E-9.
We are now ready to initialize the query.
#ifdef AXOM_USE_MPI
rc = quest::inout_init(fileName, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
#else
rc = quest::inout_init(fileName);
#endif
The variable fileName is a std::string that indicates a triangle
mesh file. Another overload of quest::inout_init() lets a user code pass
a reference to a mint::Mesh* to query meshes that were previously read in
or built up. If initialization succeeded (returned
quest::QUEST_INOUT_SUCCESS), the code can
- Query the mesh bounds with
quest::inout_mesh_min_bounds(double[3])andquest::inout_mesh_max_bounds(double[3]). - Find mesh center of mass with
quest::inout_mesh_center_of_mass(double[3]). - Test if a query point is inside the mesh surface. In this example
ptis adouble[3]andnumInsideis a running total.
const double x = pt[0];
const double y = pt[1];
const double z = pt[2];
const bool ins = quest::inout_evaluate(x, y, z);
numInside += ins ? 1 : 0;
Once we are done, we clean up with the following command:
quest::inout_finalize();
Signed Distance query C API¶
Excerpted from <axom>/src/axom/quest/examples/quest_signed_distance_interface.cpp.
Quest header:
#include "axom/quest.hpp"
Before initialization, a code can set some parameters for the distance query.
- Passing
truetoquest::signed_distance_set_closed_surface(bool)lets the user read in a non-closed “terrain mesh” that divides its bounding box into “above” (positive distance to the surface mesh) and “below” (negative distance). quest::signed_distance_set_max_levels()andquest::signed_distance_set_max_occupancy()control options for the BVH tree spatial index used to accelerate signed distance queries.- If the SLIC logging environment is in use, passing
truetoquest::signed_distance_set_verbose()will turn on verbose logging. - Use of MPI-3 shared memory can be enabled by passing
truetoquest::signed_distance_use_shared_memory().
The distance query must be initialized before use. In this example,
Arguments is a POD struct containing parameters to the executable.
As with the in/out query, a user code may pass either a file name or a
reference to a mint::Mesh * to quest::signed_distance_init().
int rc = quest::signed_distance_init(args.fileName, global_comm);
Once the query is initialized, the user code may retrieve mesh bounds
with quest::signed_distance_get_mesh_bounds(double* lo, double* hi).
Test query points against the mesh with quest::signed_distance_evaluate().
Here, pt is a double[3], phi is a double array, and inode
is an integer.
phi[inode] = quest::signed_distance_evaluate(pt[0], pt[1], pt[2]);
Finally, clean up.
quest::signed_distance_finalize();